Mashroo3k Consulting offers a comprehensive feasibility study for an iron recycling plant project in the Sultanate of Oman, offering the highest return on investment and the best payback period. This study is based on a thorough study of the industrial sector in the Sultanate of Oman, an analysis of competitors’ strategies, and the provision of competitive pricing.

The iron recycling plant sorts the iron and separates it from any mixed materials, then cuts and melts it, casting it into raw and pure iron bales. The plant relies on the recycling of used iron, old iron, scrap iron, and damaged iron. The plant targets iron and steel factories and aluminum product factories. mashroo3k Consulting Company advises investors who wish to invest in an iron recycling plant project, or develop their existing projects, to seek the advice of specialized consultants through mashroo3k Company, to help them determine the best methods to achieve the highest profit return and the best payback period.



Products that meet international quality standards.
Latest manufacturing and packaging technology.
A creative and innovative marketing team.
A management team with ambitious plans.
Executive summary
Study project services/products
Market Size Analysis
Risk Assessment
Technical study
Financial study
Organizational and administrative study

Technological advancements in the GCC, coupled with population growth, have contributed to an increase in the amount of waste generated from human and industrial activities, among other things. This waste has put GCC governments to a real test; they must address it more quickly to avoid environmental and health problems. The total amount of waste collected (hazardous and non-hazardous) in the GCC is estimated at 131.8 million tons, with 1.2% being hazardous waste and 98.8% being non-hazardous waste. Mashroo3k Economic and Management Consulting would like to present the following key indicators for the recycling sector in the GCC:
The total amount of hazardous waste collected in the GCC amounted to 1.6 million tons.
The total amount of non-hazardous waste in the GCC amounted to 2 million tons.
Collected hazardous waste is divided into: (6% medical waste), (81.8% industrial waste), and (12.2% other waste such as batteries and electronic waste).
Collected non-hazardous waste is divided into: (40.7% construction waste), (25% household waste), (1.7% green waste), and (32.5% other waste).
The amount of treated waste of the total collected waste amounted to 51% (67.2 million tons).
The amount of industrial waste collected in the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) countries is equal to 1.3 million tons. It is worth noting that Saudi Arabia and the UAE alone produce 63.1% and 19.3%, respectively, of this total waste.
The amount of non-hazardous waste collected from the household sector in the Gulf Cooperation Council countries amounted to 32 million tons.
The UAE ranks first in the amount of waste treated through recycling, at 42.8%.
The amount of hazardous waste recycled in GCC countries amounts to 100,000 tons (9.3%) of the total hazardous waste treated.
Saudi Arabia leads in solid waste volume, generating more than 16 million tons annually, followed by the UAE with approximately 5.4 million tons annually.
Waste in the Middle East and North Africa is divided into the following:
Food and green waste: 58%
Glass: 3%
Metals: 3%
Paper and cardboard: 13%
Plastic: 12%
Wood: 1%
Rubber and leather: 2%
Other waste: 8%
In the GCC countries, hazardous waste is treated by incineration (9%), landfill (51.7%), and recycling (9.3%), with other methods accounting for the remaining 30%.
Non-hazardous waste in the GCC is treated by landfill (51%), while other methods, such as incineration and recycling, account for 49%. Advantages of the circular economy in the GCC:
_ Reducing primary energy consumption by approximately 4%.
_ Creating 50,000 jobs in the recycling sector.
_ Reducing carbon dioxide emissions by 13 million tons annually.
_ Contributing to achieving economic returns of up to $138 billion for the GCC countries between 2020 and 2030.
Recommendations:
Mashroo3k recommends investing in the recycling sector due to the following:
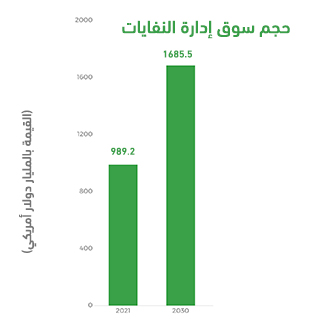
_ The world produces approximately 2.01 billion tons of municipal solid waste, and this volume is expected to reach 3.40 billion tons by 2050.
_ In 2014, global e-waste production reached 12.8 million metric tons, and this figure increased to 53.6 million metric tons by 2019.
Plastic and paper account for approximately 29% of the total global waste and are two promising sectors if invested in through recycling. Below is a breakdown of all waste and its percentage of the total global waste:
Kingdom of Saudi Arabia:
There are 1,801 factories under construction in Saudi Arabia. The number of licensed workers in these factories is estimated at approximately 78,650. The capital of these factories amounts to 68,481 million riyals.
The Riyadh region accounts for 40.4% of the total factories under construction (728 factories).
United Arab Emirates:
The industrial sector in the UAE contributes approximately 8.4% of the GDP.
The value of industrial exports currently exceeds AED 240 billion.
The UAE aspires to be ranked 25th in the Global Manufacturing Competitiveness Index, having previously ranked 38th.
The country’s strategy supports the establishment and establishment of 13,500 small and medium-sized enterprises.
The industrial sector in the UAE contributes approximately 8.4% of the GDP.
Kuwait:
The number of establishments with more than 20 employees has reached 549. The number of employees in these establishments reached 129,735. The total production value of these establishments amounted to 35,566,260 thousand Kuwaiti dinars.
Qatar:
The manufacturing industry contributes approximately 9.2% of the GDP. Establishments with fewer than 10 employees equal 1,799, with 8,305 workers.
Establishments with more than 10 employees equal 1,668, with 153,567 workers in these establishments.
Sultanate of Oman:
The contribution of manufacturing exports to the Sultanate’s total exports is 31.4%.
The manufacturing industry’s growth rate is estimated at approximately 6% over the past five years.