تعد دراسة جدوى مدرسة عالمية خطوة أساسية لضمان نجاح المشروع؛ حيث تبدأ بقياس حجم الطلب على التعليم الدولي وتحليل مؤشرات السوق لتحديد احتياجات الشرائح المستهدفة، يساعد ذلك الأمر في تطوير منهجية تتبنى إيجاد مناهج تعليمية متقدمة تلبي تطلعات أولياء الأمور فضلاً عن وضع استراتيجية تسويقية فعالة من شأنها إبراز جودة التعليم والتنوع الثقافي الذي تقدمه المدرسة، مما يعزز من جاذبيتها وقدرتها على استقطاب الطلاب. على المستوى الفني، تركز الدراسة على اختيار موقع استراتيجي يضمن سهولة الوصول، مع توافر بنية تحتية متكاملة تدعم العملية التعليمية. كما تشمل تجهيز المدرسة بأحدث التقنيات والوسائل الحديثة التي تعزز أساليب التدريس التفاعلي. أما بخصوص الجانب المالي، فتتضمن تحليلًا شاملاً لتكاليف الإنشاء والتشغيل، مع تقدير الإيرادات المتوقعة لضمان استدامة المشروع وتحقيق العوائد المجزية.

The International School project represents an advanced educational environment because it offers internationally accredited academic programs, ensuring high-quality education that keeps pace with global developments. This school is distinguished by its ability to develop students’ skills and promote cultural diversity by integrating students of different nationalities into a comprehensive educational environment. It also contributes to preparing students academically and professionally through modern curricula and educational techniques. It is noteworthy that the school provides an integrated educational experience covering all academic levels, from kindergarten to high school. The school pays special attention to extracurricular activities, including sports, arts, and cultural programs, to ensure students’ academic and personal development. To achieve this distinguished level of education, a feasibility study for an international school is an essential step in evaluating various aspects of the project, starting from studying the needs of the target community, through financial and administrative planning, and finally ensuring the project’s sustainability and the achievement of its investment objectives.

Accredited international curricula
Multilingual education.
Extracurricular activities such as sports, arts, and culture
Advanced educational technologies.
Academic support programs.
Consulting and educational services.
Modern and advanced facilities.
Trips and student exchange programs


Accredited international curricula that meet global standards.
Comprehensive development of students’ skills.
A multicultural learning environment.
Highly qualified and competent faculty.
Using modern educational technologies.
Extracurricular activities that enhance personal capabilities.
Modern and fully equipped facilities.
Preparing students for international universities.
Executive summary
Study project services/products
Market Size Analysis
Risk Assessment
Technical study
Financial study
Organizational and administrative study
The Education Sector in the GCC Countries
Believing in the importance of the education sector and its role in promoting the localization of the national workforce, Mashroo3k for Economic Consultancy and Market Research is pleased to present the following key indicators of the education sector in the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) countries, inviting investment in this vital field:
The total number of students in Early Childhood Development (including nurseries and kindergartens) across the GCC reached approximately 851,500 students, according to the latest available statistics.
The number of students enrolled in school education stages across the GCC is estimated at around 9.3 million students (79.4% in the public sector and 20.6% in the private sector).
The number of learners in adult education centers is estimated at 181,247 students.
The number of students enrolled in higher education institutions stands at 2,206,446 students.
The number of early childhood teachers is approximately 50,647.
The number of school education teachers is estimated at around 727,904.
There are 5,806 operational early childhood education institutions.
There are 32,310 operational school education institutions.
Over the past years, GCC governments have actively sought to bridge the gap between education and the labor market by adopting educational curricula that emphasize vocational and technical education and encourage learning through modern technologies and digital platforms. It is also worth noting the increasing investment in education quality across the six countries to produce graduates who meet the private sector’s workforce requirements.
According to the latest statistics:
Saudi Arabia allocates 18.9% of its budget to education.
The UAE allocates 14.8% of its budget to education.
Oman allocates 12.2% of its budget to education.
Bahrain allocates 9.8% of its budget to education.
Kuwait allocates 12.3% of its budget to education.
Qatar allocates 10.5% of its budget to education.
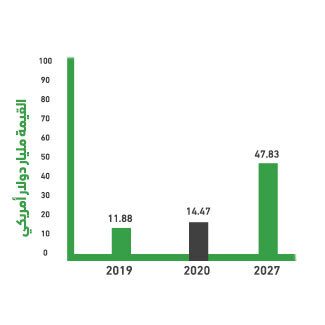
By 2023, the value of the private education market in the GCC is expected to reach USD 26.2 billion.
The Global Education Sector
The global education services market was valued at approximately USD 2,882.52 billion by the end of 2021. Experts project that the market will reach USD 3,191.79 billion by the end of 2022, achieving a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 10.7%. Furthermore, by 2026, the market value is expected to rise to USD 4,623.90 billion, reflecting a CAGR of 9.7% over the forecast period.

Investment in the Saudi private education sector grew by 3% in 2016, rising to 15.5% compared to 12.5% in 2015. Investment in the private education sector has increased over the past five years, reaching approximately 10 billion riyals.